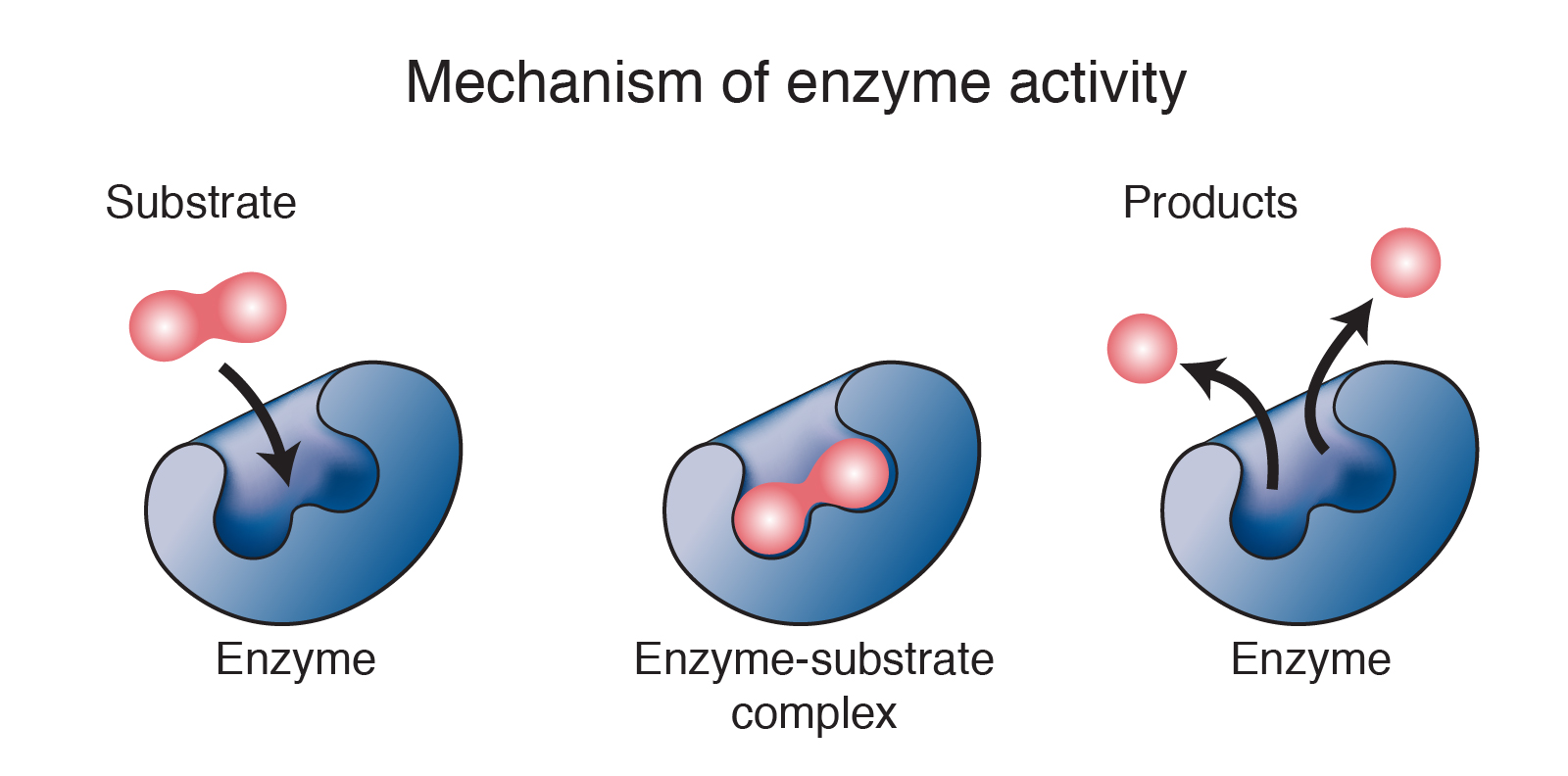
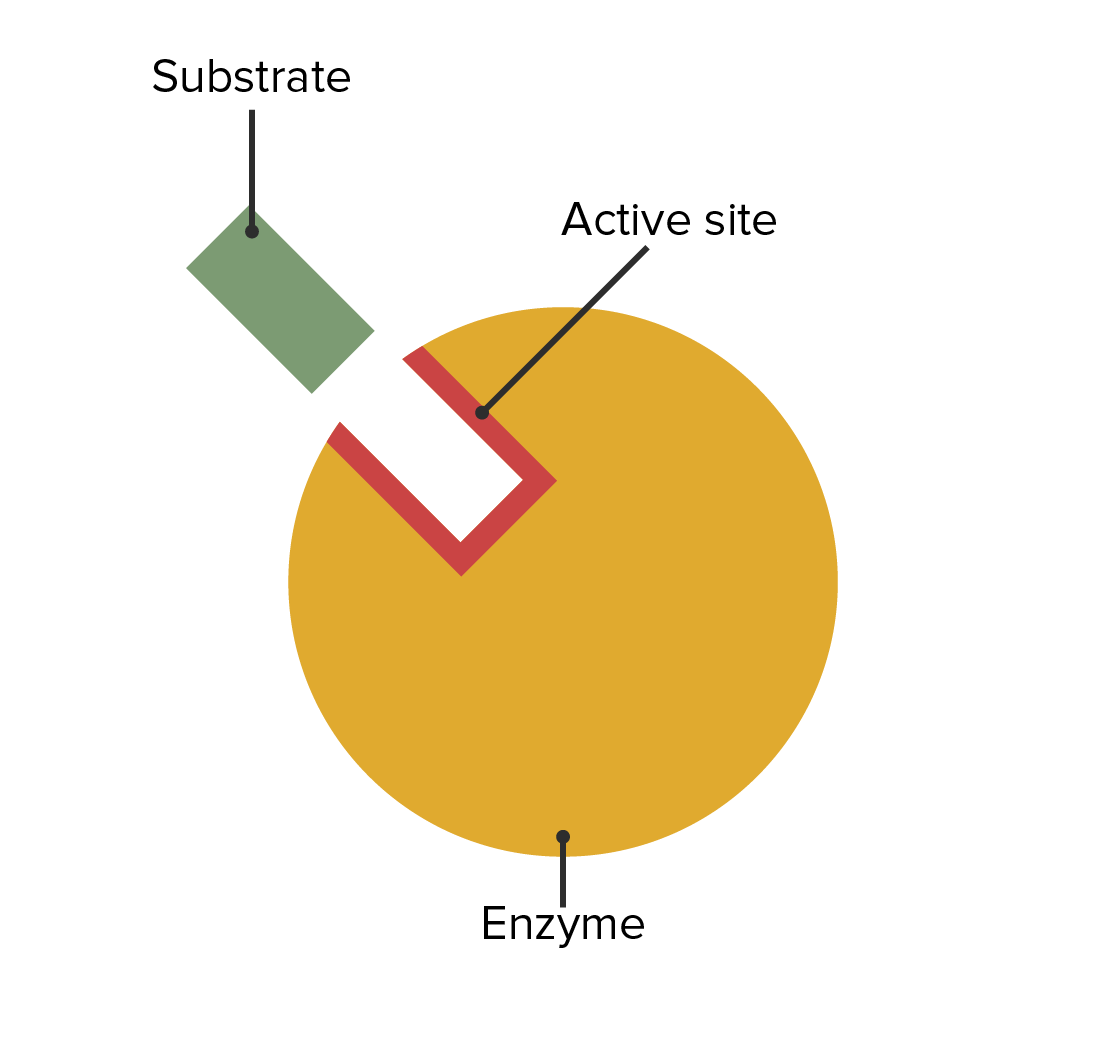
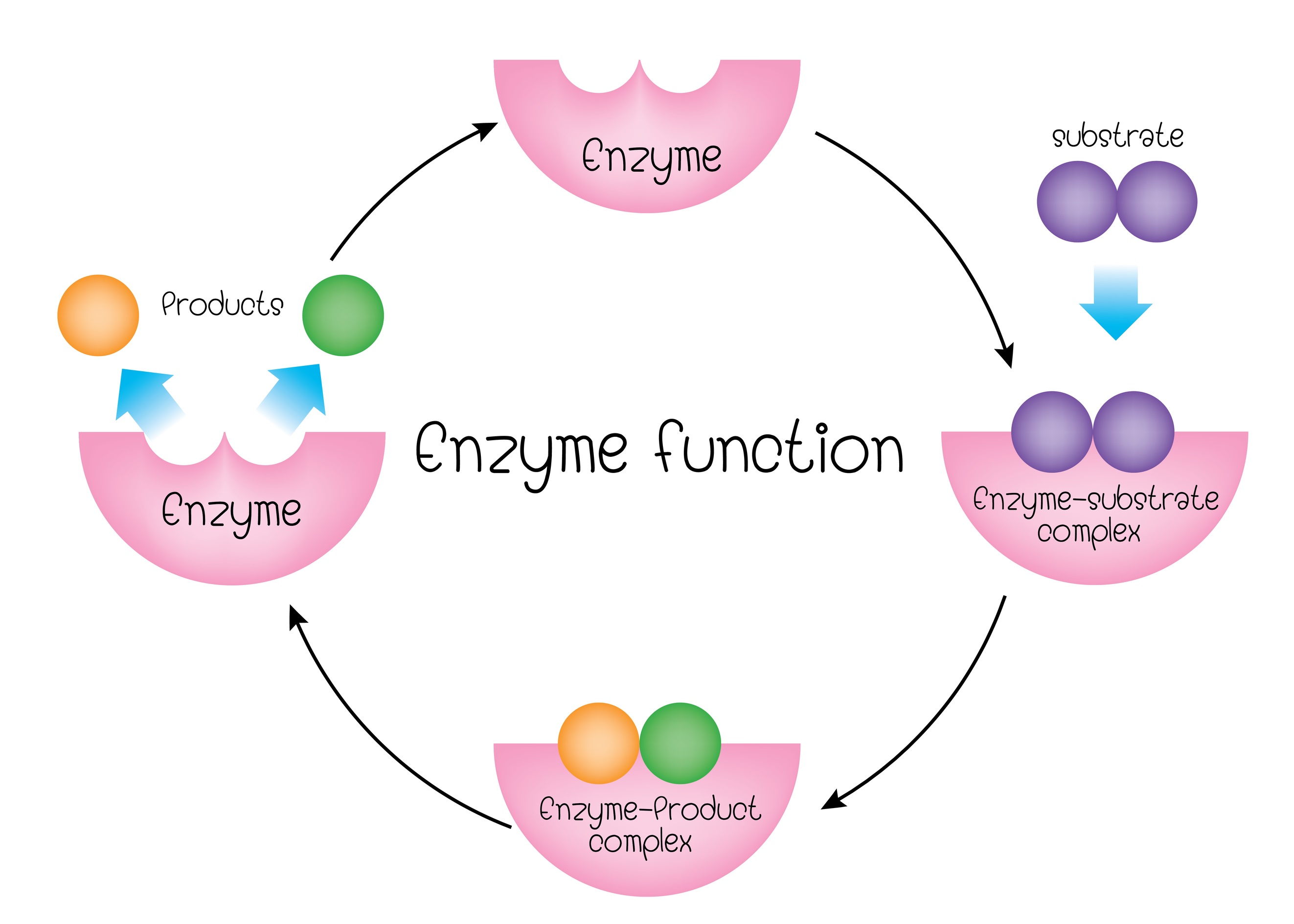
Metabolic processes and other chemical reactions in the cell are carried out by a set of enzymes that are necessary to sustain life. The enzyme is not destroyed during the reaction … Enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. An enzyme devoid of a cofactor is an apoenzyme, while an enzyme with its cofactor is called a holoenzyme. · enzymes are protein macromolecules that are necessary to initiate or speed up the rate of chemical reactions in the bodies of living organisms. This ai-generated answer is powered by openai. You should not rely on this feature for medical, financial, or legal advice. · cofactors are essential for the functioning of the enzyme. Since they are not destroyed during the process, a cell can reuse each enzyme repeatedly. They speed up the chemical reactions required for life by lowering the activation energy, all without being consumed in the process. · enzymes are substances in the body that cause and speed up crucial chemical reactions. An enzyme (/ ˈɛnzaɪm /) is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst, accelerating chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. What are enzymes? For example, elevated liver enzymes could be a sign of liver disease. · enzyme , a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. The sequence of amino acids specifies the structure, which in turn identifies the catalytic activity of … Enzymes are a linear chain of amino acids, which give rise to a three-dimensional structure. Your healthcare provider can use a variety of enzyme and protein blood tests to check for certain health conditions. The enzyme is not destroyed during the reaction and is used over and over. Most critically, enzymes catalyze all … They can also be extracted from cells and then used to catalyse a wide range of commercially important processes. “enzymes can be defined as biological polymers that catalyze biochemical reactions. ” the majority of enzymes are proteins with catalytic capabilities crucial to perform different processes. Too much or too little of a certain enzyme can cause health problems. · enzymes provide help with facilitating chemical reactions within each cell. Enzymes in our blood can also help healthcare providers check for injuries and diseases. 8. 1. 3 examples are lactase, alcohol … It speeds up the rate of a specific chemical reaction in the cell. There are many types of enzymes, and most enzymes are proteins. Enzymes are proteins that help speed up chemical reactions in our bodies. Creating an answer for you using ai. Structure of enzyme enzymes are proteins that are made up of several … They are found in all living cells that vary in type based on the function it performs. · enzymes have a specific method of action (lock-and-key mechanism and enzyme fit hypothesis). An enzymes name is often derived from its substrate or the chemical reaction it catalyzes, with the word ending in -ase. Enzymes are essential for digestion, liver function and much more. · ions are inorganic molecules that loosely bond to the enzyme to ensure it can function. · an enzyme is a biological catalyst and is almost always a protein. · enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. The molecules on which enzymes act are called substrates, and the substance formed is called the product. Ai-generated content may sometimes contain inaccurate, incomplete, or biased information, so make sure you do additional research. By contrast, coenzymes are organic molecules that also loosely bond with and allow … Enzymes ’ function is to help trigger bodily processes ranging from digestion to blood clotting to growth. The molecules on which enzymes act are called substrates, which are converted into products. Generally, higher enzyme concentrations lead to faster reaction rates because more enzyme molecules are available to catalyze the conversion of substrates to products. · enzyme (noun): · enzymes are specialized proteins (and in some cases rna molecules) that act as catalysts in living organisms. Most critically, enzymes catalyze all aspects of cell metabolism. A biological macromolecule, typically a protein (and occasionally an rna molecule), that acts as a catalyst to accelerate a specific chemical reaction by … A cell contains thousands of different types of enzyme molecules, each specific to a particular chemical reaction.
Enzyme Names: The 3 Letter Ending You Need To Know
Metabolic processes and other chemical reactions in the cell are carried out by a set of enzymes that are necessary to sustain life. The enzyme...